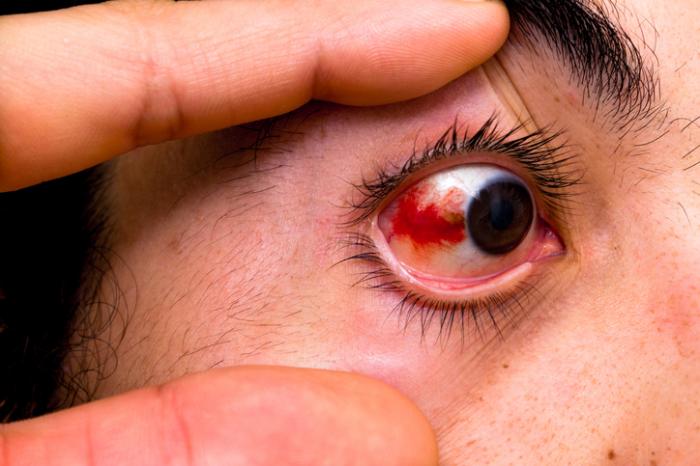
Bloodshot Eyes or Red Eyes
Bloodshot eyes or Red eyes occurs when the vessels in your eye become swollen or irritated. They are usually caused by allergy, eye fatigue, over-wearing contact lenses or common eye infections such as pink eye (conjunctivitis).
Redness of the eye, also called bloodshot eyes, can signal a more serious eye condition or disease, such as uveitis or glaucoma. However, most serious eye problems happen when you have redness along with pain or changes in your vision.
What are the common causes of bloodshot eyes?
The most common cause of eye redness is inflamed vessels on the surface of the eye.
Irritants
Various irritants can cause vessels on the eye to become inflamed, including:
- dry air
- exposure to the sun
- dust
- allergic reactions
- colds
- bacterial or viral infections, such as measles
- coughing
Eyestrain or coughing can cause a specific condition known as subconjunctival hemorrhage. When this occurs, a blood blotch may appear in one eye. The condition may look serious. However, if it’s not accompanied by pain, it’ll typically clear up in 7 to 10 days.
Eye infections
More serious causes of eye redness include infections. Infections can occur in different structures of the eye and typically produce additional symptoms such as pain, discharge, or changes in your vision.
Infections that can cause eye redness include:
- inflammation of the follicles of the eyelashes, called blepharitis
- inflammation of the membrane that coats the eye, called conjunctivitis or pink eye
- ulcers that cover the eye, called corneal ulcers
- inflammation of the uvea, called uveitis
Other causes of bloodshot eyes or eye redness include:
- trauma or injury to the eye
- a rapid increase in eye pressure that results in pain, called acute glaucoma
- scratches of the cornea caused by irritants or overuse of contact lenses
- inflammation of the white part of the eye, called scleritis
- eyelid styes
- bleeding problems
- rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- marijuana use
When should you contact your doctor?
Most causes of eye redness don’t warrant emergency medical attention.
If you experience eye redness, you should make an appointment to see your doctor if:
- your symptoms last longer than 1 week
- you experience changes in your vision
- you experience pain in your eye
- you become sensitive to light
- you have discharge from one or both of your eyes
- you take medications that thin your blood, such as heparin or warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven)
Even though most causes of eye redness aren’t severe, you should seek emergency medical help if:
- your eye is red after trauma or injury
- you have a headache and have blurry vision
- you begin seeing white rings, or halos, around lights
- you experience nausea and vomiting
How can the symptoms of bloodshot eyes be treated?
If your eye redness is caused by a medical condition such as conjunctivitis or blepharitis, you may be able to treat your symptoms at home. Warm compresses on the eye can help reduce the symptoms of these conditions.
You should also make sure that you wash your hands frequently, avoid wearing makeup or contacts, and avoid touching the eye.
If your eye redness is accompanied by pain or changes in vision, you need to see your doctor for treatment.
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms, your current health conditions, and problems that may have caused irritation to your eye. Your doctor may also examine your eye and use a saline solution to wash out any irritants in your eye.
Depending on your diagnosis, your doctor may prescribe treatment that helps to alleviate your symptoms. This would likely include antibiotics, eye drops, and home care as described above.
In some cases, where the eye is very irritated, your doctor may suggest wearing a patch to limit light exposure and help your eye heal.
What are the complications of bloodshot eyes?
Most causes of eye redness won’t result in serious complications.
If you have an infection that causes vision changes, this may affect your ability to perform basic tasks such as cooking or driving. Vision impairments in these areas can result in accidental injury.
Infections that aren’t treated may also result in permanent damage to the eye.
If eye redness doesn’t resolve in 2 days, you should call your doctor.
How can you prevent bloodshot eyes?
Most cases of eye redness can be prevented by using proper hygiene and avoiding irritants that can cause redness.
Follow these tips to prevent eye redness:
- Wash your hands if you’re exposed to someone who has an eye infection.
- Remove all makeup from your eyes each day.
- Don’t wear contact lenses longer than recommended.
- Clean your contact lenses regularly.
- Avoid activities that can cause eyestrain.
- Avoid substances that can cause your eyes to become irritated.
- If your eye becomes contaminated, flush it out immediately with eyewash or water if eyewash isn’t available.
Source: healthline.com
